Gel electrophoresis is a scientific technique used to separate DNA, RNA, or proteins based on their size and electrical charge. In this process, the molecules are placed in a gel and an electric current is applied. The molecules move through the gel at different speeds, depending on their size and charge: smaller or more negatively charged molecules move faster. This separation allows scientists to analyze the specific characteristics of these molecules, which is crucial in research, medical diagnostics, and forensic science. Gel electrophoresis involves the use of two types of gel: Agarose (used for DNA/RNA separation), and Polyacrylamide gel (used in protein analysis and DNA sequencing). Some of the examples of gel electrophoresis in real life are as follows:
Examples
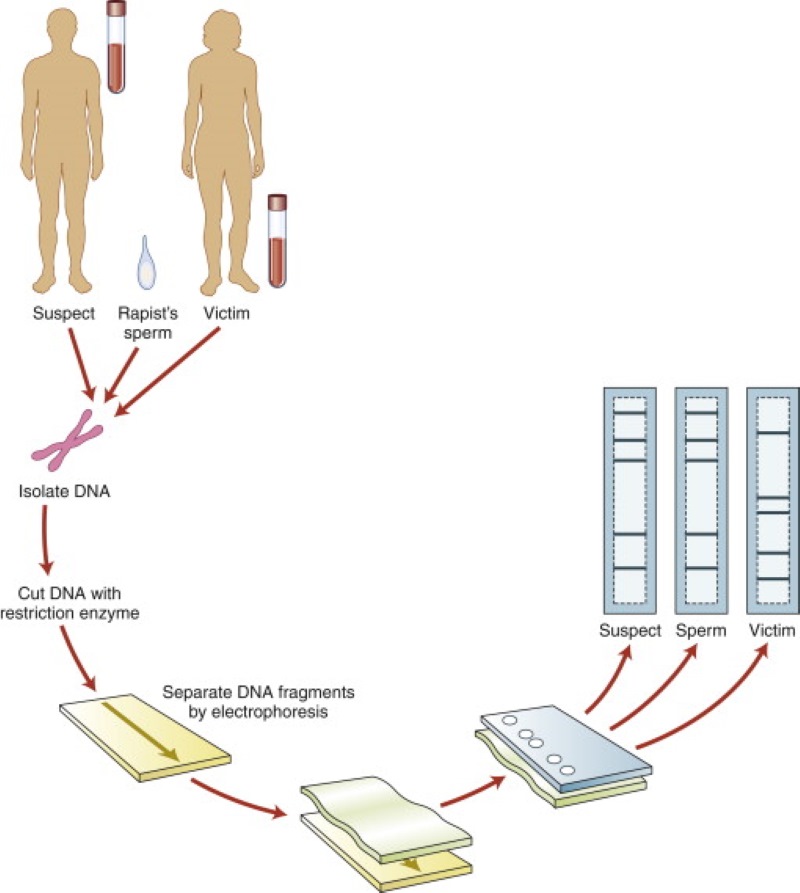
1. Forensic Science for DNA Analysis
In criminal investigation, gel electrophoresis is used to analyze DNA samples found at crime scenes. It helps in comparing the DNA from the sample with that of a suspect. The process involves extracting DNA from samples (like blood, hair, or skin cells), cutting it into smaller pieces, and running it through a gel. Different DNA pieces move at different speeds, creating a unique pattern (like a barcode) for each individual, which can be compared for identification.
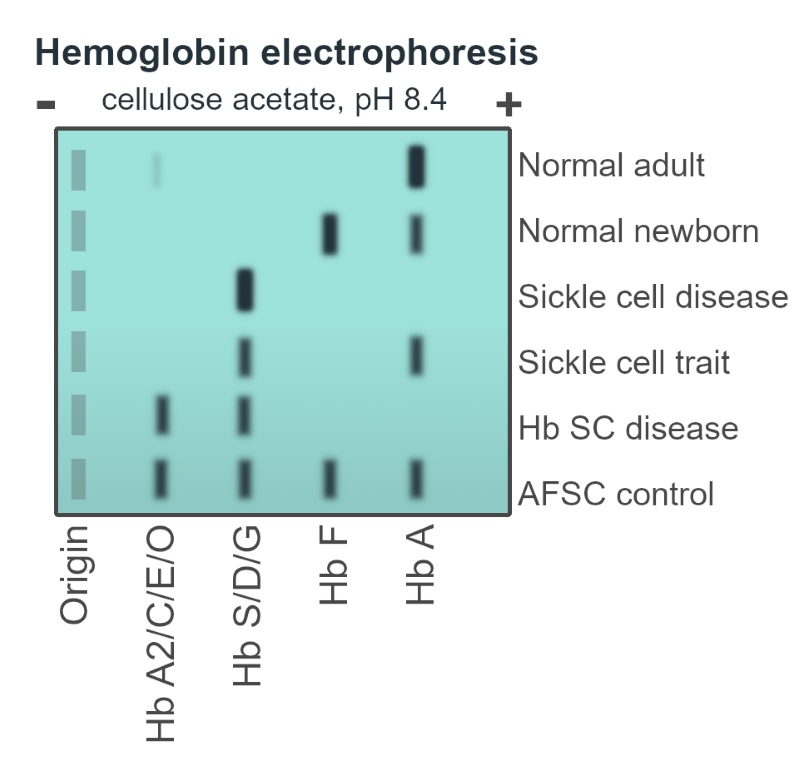
2. Medical Diagnostics for Disease Identification
Doctors use gel electrophoresis to diagnose diseases caused by genetic mutations. For instance, in conditions like sickle cell anaemia, the structure of haemoglobin protein in the blood changes. By running a patient’s blood proteins through a gel, doctors can see if the haemoglobin pattern matches that of normal or sickle cell anaemia haemoglobin, aiding in diagnosis.
3. Biological Research for Gene Analysis
Scientists studying genetics use gel electrophoresis to analyze genes and their functions. For example, when researchers want to understand which genes are involved in a disease, they can compare the DNA from healthy and diseased cells using gel electrophoresis. The differences in the patterns on the gel can indicate which genes may be causing the disease.
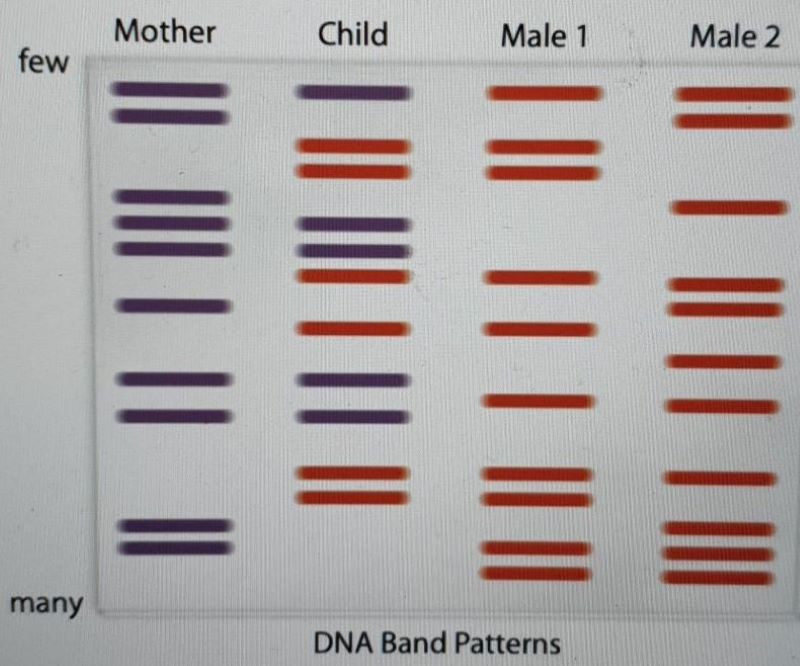
4. Paternity Testing
In paternity cases, gel electrophoresis is used to compare the DNA of a child with that of the alleged father. Each person’s DNA has a unique pattern, and a child’s DNA is a combination of patterns from both parents. By comparing these patterns, it can be determined if the individual is the biological parent of the child.
5. Quality Control in Biotechnology
In biotech industries, gel electrophoresis is essential for quality control. For example, when producing recombinant proteins (like insulin), this method is used to verify the size and purity of the product. Consistent band patterns on the gel indicate a pure and correctly sized protein, ensuring the product meets industry standards.
6. Virus Identification
Gel electrophoresis is used in virology to identify and compare genetic material olf viruses. When dealing with outbreaks of viral diseases, scientists can extract viral RNA or DNA and analyze it using this technique. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, electrophoresis was used to study the genetic material of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, helping in understanding its structure and mutations.
7. Food Industry Testing
In the food industry, gel electrophoresis is employed for quality control and testing the authenticity of products. For example, to verify if a product labelled as “100% beef” is indeed pure beef, DNA from the meat can be compared to known beef DNA samples using electrophoresis. This method helps in detecting adulteration or mislabeling of food products.
8. Environmental Monitoring
This technique is used for environmental monitoring, such as analyzing microbial communities in water, soil, or extreme environments. By extracting and separating DNA from environmental samples, scientists can identify the types of microorganisms present and assess the ecological health or pollution levels of an area. This technique helps in identifying and cataloguing microorganisms, many of which cannot be cultured in the lab.
9. Drug Development and Testing
In pharmaceuticals, gel electrophoresis is crucial for drug development and testing. For instance, when developing a new drug, this method can be used to analyze the purity of the compounds produced. It ensures that the final product is free from unwanted or harmful impurities.
10. Personalized Medicine
Gel electrophoresis plays a role in personalized medicine, especially in pharmacogenomics, which studies how genes affect a person’s response to drugs. By analyzing a patient’s DNA, doctors can tailor drug treatments based on how well the patient’s body can process or respond to certain medications, leading to more effective and safer treatment plans.
11. Cancer Research
Gel electrophoresis is instrumental in cancer research, particularly in the study of oncogenes (cancer-causing genes) and tumour suppressor genes. By comparing the DNA or protein profiles of cancerous cells with those of healthy cells, researchers can identify specific genetic changes that cause cancer. This information is crucial for developing targeted cancer treatments and understanding the disease’s progression.
12. Agricultural Biotechnology
In agricultural biotechnology, gel electrophoresis is used for genetic engineering of crops. Scientists can isolate and analyze genes responsible for desirable traits in plants, such as drought resistance or improved nutritional content. By confirming the successful incorporation of these genes into plant genomes, researchers can develop crops that are more resilient and nutritious.
13. Species Identification and Biodiversity Studies
Biologists use gel electrophoresis to study biodiversity and identify species, particularly in cases where species are visually similar or in different life stages. By analyzing DNA samples, scientists can accurately identify and classify various species, aiding in conservation efforts and understanding ecological relationships.
14. Prenatal Screening for Genetic Disorders
This technique is used in detecting genetic disorders in prenatal and newborn screening. For instance, disorders like Thalassemia and Cystic Fibrosis can be identified by analyzing specific DNA fragments or proteins. Early detection allows for timely intervention and management of these conditions.
15. Study of Evolutionary Relationships
Gel electrophoresis is also used in studying evolutionary relationships among species. By comparing DNA or protein sequences across different species, scientists can construct phylogenetic trees that depict the evolutionary connections and distances. This helps in understanding how species have evolved and diverged over time.
16. Infectious Disease Research
Gel electrophoresis is critical in studying infectious diseases. By analyzing the genetic material of pathogens like bacteria and viruses, researchers can understand their mechanisms of infection and resistance to drugs. For example, in tuberculosis research, electrophoresis helps identify different strains of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium and their resistance patterns to antibiotics.
17. Protein Purification in Biochemistry
In biochemistry, gel electrophoresis is used for protein purification. After expressing a protein in a laboratory setting, scientists use this technique to ensure that the protein has been correctly synthesized and is free from contaminants. This step is crucial in the production of enzymes, antibodies, and other proteins for research and therapeutic use.
18. Monitoring HIV/AIDS Treatment
In the management of HIV/AIDS, gel electrophoresis is used to monitor the effectiveness of antiretroviral therapy. By assessing the viral load and the genetic mutations of the HIV virus, healthcare providers can adjust treatments to ensure they are effective against the specific strains of the virus present in a patient.
19. Archaeology and Paleontology
Gel electrophoresis has applications in archaeology and palaeontology for analyzing ancient DNA (aDNA) from archaeological finds or fossilized remains. This technique helps in understanding the genetics of ancient populations, species evolution, and the relationships between extinct and existing species.
20. Detection of Genetically Modified Organisms
In the food and agriculture sector, gel electrophoresis is employed to detect and confirm the presence of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in crops and food products. By comparing the DNA profiles of a given sample with known GMO and non-GMO profiles, scientists can determine whether a crop or product has been genetically modified.
21. Drug Resistance Monitoring
In the field of infectious diseases, particularly for bacteria and parasites, gel electrophoresis is used to monitor drug resistance. By analyzing the genetic changes in pathogens, this technique helps in identifying mutations that confer resistance to antibiotics or other drugs, which is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies.
22. Neuroscience Research
In neuroscience, researchers use gel electrophoresis to study proteins involved in brain function and neurological disorders. For example, it can be used to analyze protein aggregation in diseases like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s, aiding in the understanding of these conditions and the development of potential therapies.
- 22 Examples of Gel Electrophoresis in Real Life - October 13, 2025
- 14 Examples of Natural Selection in Real Life - October 13, 2025
- 24 Examples of Population Genetics - October 13, 2025